A ceramic phosphor is a solid element composed of a high density color converter made using powder phosphors and functional materials. Conventional LEDs use phosphor powders encapsulated in polymers as color converters. Compared to polymer-encapsulated phosphors, ceramic phosphor plates generally show superior properties with regards to thermal stability, thermal conductivity, and long-term degradation and CIE color coordinate changes. Solid ceramic phosphors can avoid many of the high power density limitations but can have limitations in terms of light extraction and thermal quenching.
Phosphor in Glass (PiG) can also overcome some of these limitations by suspending phosphor powders in a transparent glass matrix. While PiG converters can deliver better thermal performance compared to polymer-based (silicone) systems, they are still considered insufficient for most high power white laser applications. Ceramic phosphor systems can instead lead to improved efficacy and color stability in high power phosphor-converted LED (pcLED) or laser-excited phosphor (LEP) devices.
Different ceramic phosphor converters can be combined with a blue (or UV) laser and/or high power LED to generate high color rendition white light. In addition, many saturated (red, green, etc.) colors can also be produced using ceramic or PiG components combined with blue or UV sources.
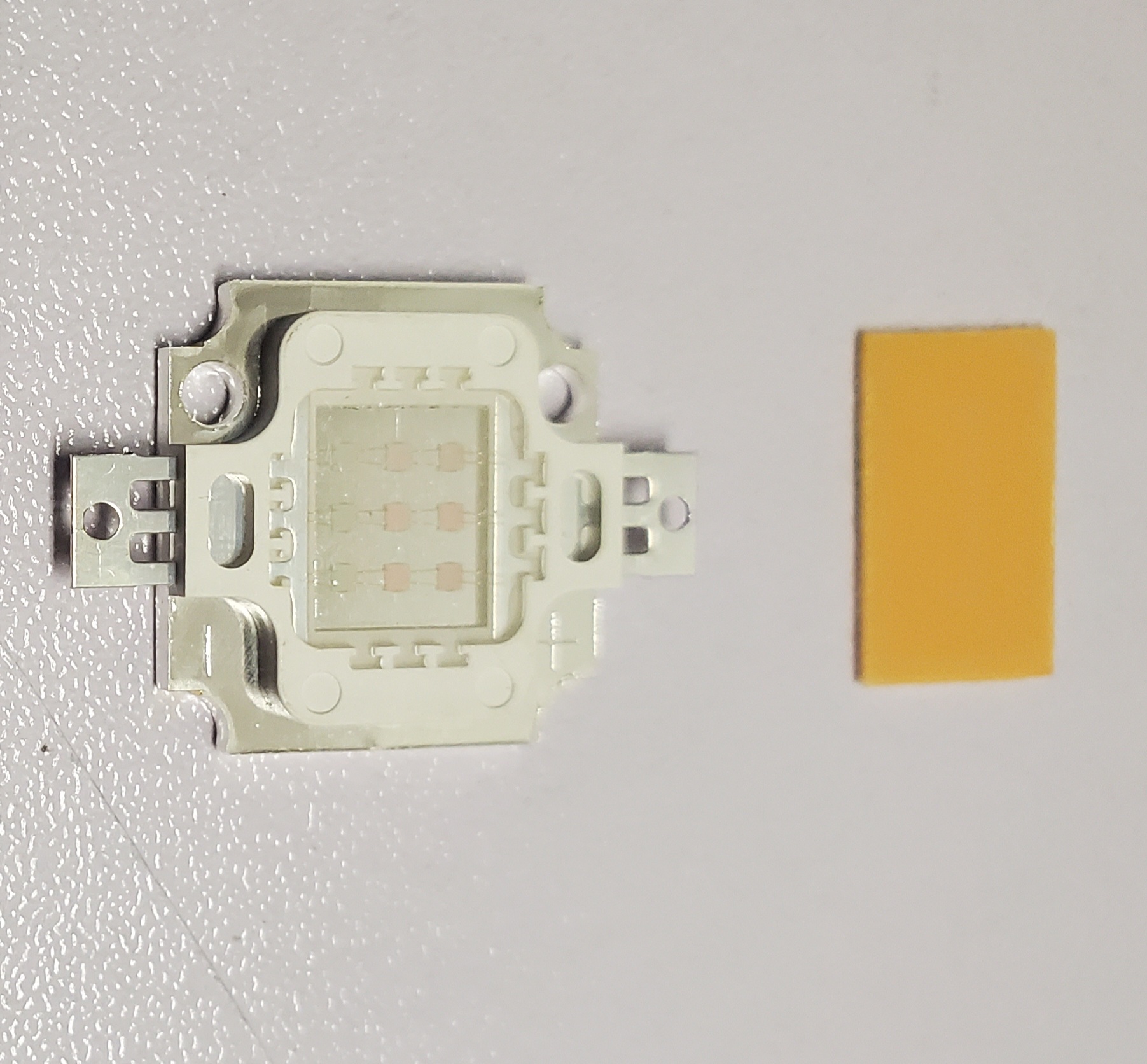
Ceramic Phosphor Plate Converters can Enhance the Thermal and Optical Stability of High Power LEDs
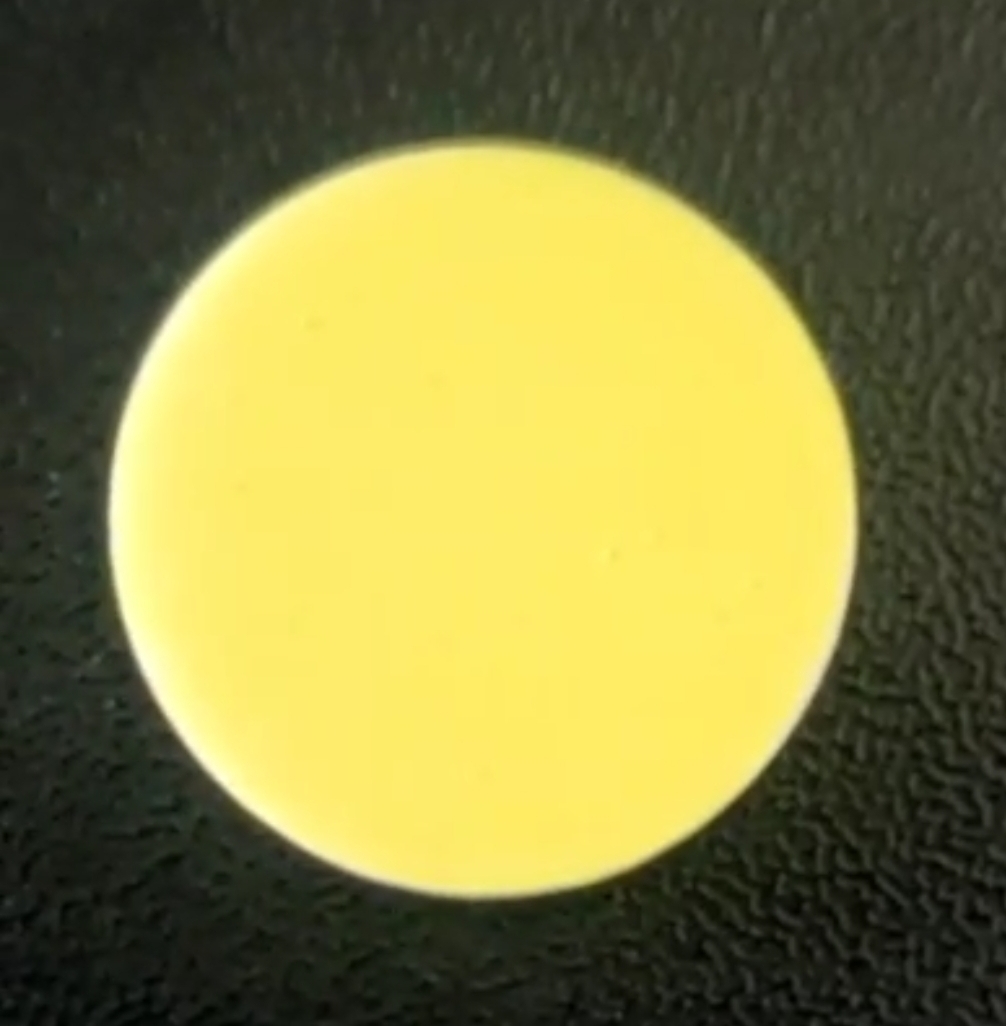

A ceramic phosphor disk with ultra-high thermal conductivity exceeding 200 W/m.K for high power lasers.